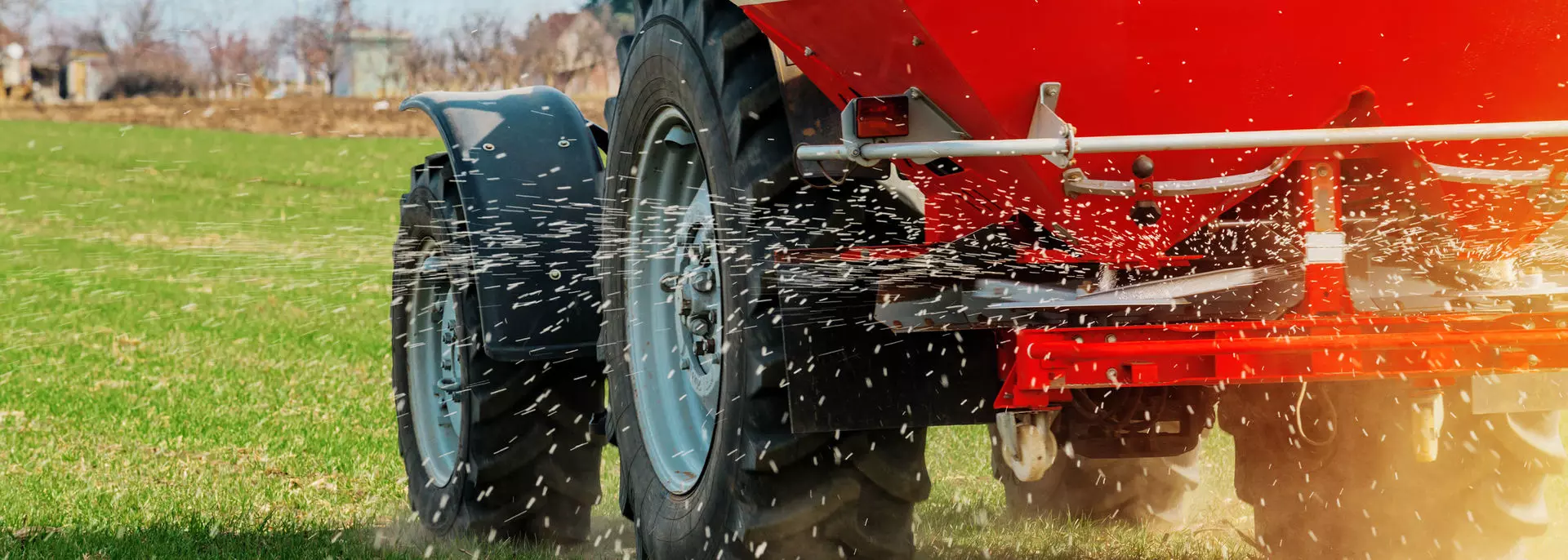
Two major requirements are placed on fertilisers: On the one hand, the agricultural industry wants to obtain an end product in which the highest possible yields can be achieved with the lowest possible material input. This is all the more important when the required capacities are very high.
On the other hand, environmental protection and sustainability are increasingly in focus. Fertilisers should be used as little as possible to relieve groundwater and maintain soil quality. Compaction and the subsequent production of granulate opens up new application possibilities for the agricultural industry.
Demands on granulate production
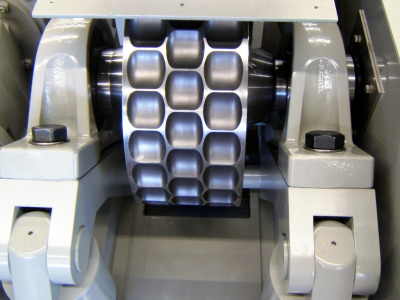
High compaction and minimum hardness
If the fertiliser is in powder form, further processing and application to the field are more difficult. The solution here is to compact the fertiliser and then produce granules. The consistency of the end product plays an important role here. High compaction and minimum hardness are crucial so that the product does not fall apart. At the same time, it must not be overcompressed so that it is suitable for possible further processing (e.g. grinding). Furthermore, the end product must not show any cracks and must be able to dissolve correctly in the soil in order to maintain the soil quality.

The production capacity of Hosokawa systems is up to 15 t/h, depending on formulation adaptations of the product to the specific end application.
Advantages of granulate production:
- Maximum compaction of the product
- Very high roller speed
- High productivity rate
- Economical process
- Reduction of operating and investment costs
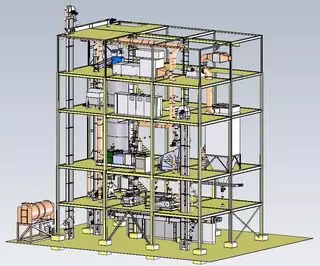
Example of a production plant for granules for fertilisers
The perfect technology for production
Roller presses especially for the chemical, food and minerals industries.
Typical areas of application:
- Chemical industry: Lignin, fertiliser
- Mineral and metallurgical industry: Sponge iron, coal, metal dust, limestone, briquetting, talc compaction
- Food industry: Compaction of protein concentrate
Read more on ARC MS & ARC SC here Series ARC MS & ARC CS